QUICK FACTS
The place is it? Massive Island, Hawaii [19.6103680, -155.4898339]
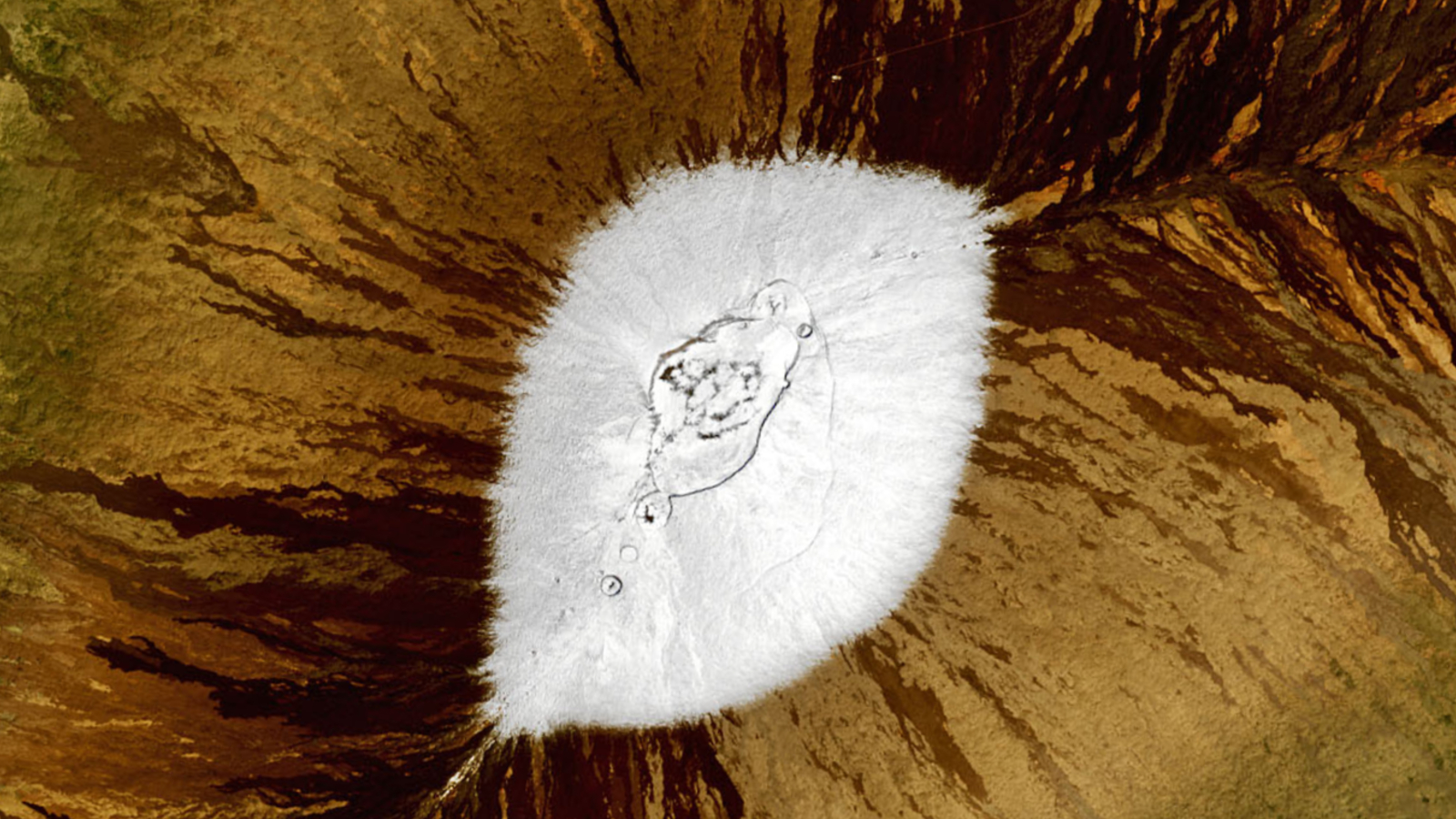
What’s within the picture? Snow masking the summit of Mauna Loa
Which satellite tv for pc took the picture? Landsat 8
When was it taken? Feb. 6, 2021
Placing satellite tv for pc images snapped in 2021 present the volcanic peaks of Hawaii’s Massive Island lined with a thick dusting of snow, additionally recognized by locals as “pineapple powder,” following one of many island’s most excessive snowfalls in current historical past.
The primary picture (see above) exhibits probably the most intensive snow protection on Mauna Loa, a 13,681-foot-tall (4,170 meters) volcano close to the middle of the Massive Island. The second picture (beneath) exhibits a barely smaller white patch on Mauna Kea, a 13,796-foot-tall (4,205 m) peak positioned round 25 miles (40 kilometers) additional north. Each pictures had been taken on the identical day.
Mauna Loa remains to be lively and most lately erupted between November and December 2022, in response to the International Volcanism Program. Mauna Kea, in the meantime, is dormant and has not erupted for no less than 4,600 years.
Hawaiian snow is extra frequent than most individuals notice, and each Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea usually obtain no less than a lightweight dusting yearly. Nevertheless, 2021 was an excessive case.
When the picture was taken, the mixed snow masking each peaks reached the second-highest quantity for this time of the yr since data started in 2001, in response to NASA’s Earth Observatory. On the peak of the previous snowstorm, as much as 2 toes (0.6 m) fell on the summit of each volcanoes in a single day.
Associated: See all the perfect pictures of Earth from house
Native studies revealed that a number of islanders traded of their surfboards for snowboards and skis, and braved the journey up Mauna Kea to partake in some uncommon snow sports activities as quickly because the roads had been cleared.
Pineapple powder
Hawaiian snow is commonly linked to a climate phenomenon known as Kona low, in response to the Earth Observatory. That is the place winds shift from the standard northeast course and begin blowing from the southwest, or “Kona” facet, drawing moisture from the tropical Pacific, which turns into rain and snow because it rises up the mountains’ slopes.
Snow is more than likely to happen between October and April, and each Mauna Loa and Mauna Kea expertise a mean of 20 days of snow cowl yearly, in response to the Lyman Museum, primarily based within the Massive Island city of Hilo. On uncommon events, snow has additionally fallen on the volcanoes as late as June, in response to The Climate Channel. Nevertheless, the pineapple powder is probably not as frequent sooner or later.

Current analysis revealed that human-caused local weather change will seemingly make snow a lot much less seemingly in Hawaii as rising sea floor temperatures make Kona low much less more likely to happen, in response to the College of Hawai’i at Manoa (UHM).
“Sadly, the projections recommend that future common winter snowfall might be 10 instances lower than current day quantities, just about erasing all snow cowl,” Chunxi Zhang, an atmospheric modeling specialist on the Worldwide Pacific Analysis Heart in Hawaii, mentioned in a UHM assertion.
In Hawaiian mythology, Mauna Kea is residence to the snow goddess Poli’ahu, who had a fierce rivalry with Pele — the goddess of fireside and volcanoes, for which the uncommon glass-like constructions that kind at Hawaii’s Kilauea volcano are named. In a single story, Poli’ahu defeated Pele in a sledding race, which brought on the latter to unleash a collection of main volcanic eruptions in anger, in response to the College of Hawai’i at Hilo.