Local weather and science correspondent
 ESA-CNES-ARIANESPACE
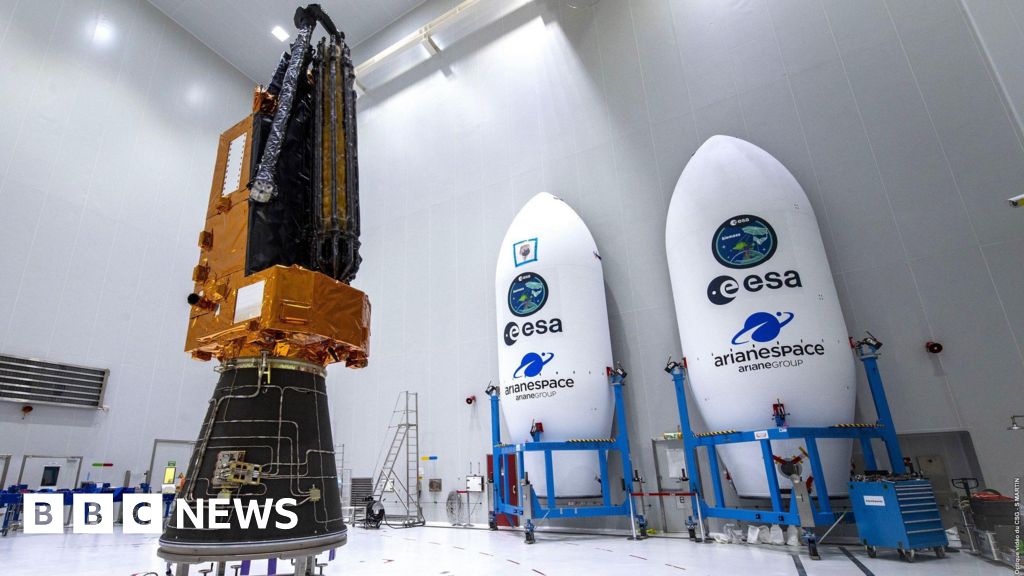
ESA-CNES-ARIANESPACEA primary-of-its-kind satellite tv for pc attributable to launch on Tuesday will be capable to see by means of clouds and leafy canopies to evaluate how they’re defending the planet from local weather change.
The Biomass satellite tv for pc, from the European House Company, will “weigh” the Earth’s forests, revealing how a lot planet-warming carbon is being saved inside timber and due to this fact saved out of the environment.
Till now the quantity of carbon saved by the 1.5 trillion timber within the planet’s rainforests has been unattainable to calculate.
Led by British firm Airbus, the undertaking hopes to assist scientists extra precisely mannequin local weather change and monitor charges of deforestation.
The satellite tv for pc is because of be launched at 10:15 BST from ESA’s Kourou station in French Guiana.
It has been affectionately named “house brolly” for its large 12m diameter antenna which expands outwards.
The antenna will use radar with a really lengthy wavelength – permitting it to see deeper inside forests and reveal branches and trunks obscured by the cover.
“Most radars that we have now in house at the moment take great photos of icebergs, however once they take a look at forests they see the tops of the forest, the little twigs, the little leaves, they do not penetrate down into the forests,” defined Dr Ralph Cordey, head of geosciences at Airbus.
“However what we discovered was that through the use of a for much longer radar wavelength, we may see down into the depths of timber and forests,” he mentioned.
The 1.2-tonne satellite tv for pc will use an strategy not dissimilar to that utilized in a CT scan, and analyse slices by means of the timber on repeat passes to construct up an image of how a lot woody materials is current.
It’s this materials that can be utilized as a proxy for the quantity of planet-warming carbon dioxide saved.
At the moment scientists have been measuring particular person timber and attempting to extrapolate, however this presents a “enormous problem” mentioned Prof Mat Disney, professor of distant sensing, at College School London.
“Our present understanding is basically patchy, as a result of it is actually, actually tough to measure,” he mentioned. “Basically, what we’re speaking about is attempting to weigh the quantity of carbon that is saved in a single and a half trillion timber throughout the tropics.
“Satellites are actually the one approach you are able to do that constantly.”
On the bottom measurements will proceed to happen after the satellite tv for pc is launched to confirm the information it’s sending again.
 ESA-CNES-ARIANESPACE
ESA-CNES-ARIANESPACERegardless of years of testing, the launch won’t be simple.
“Sure issues on the satellite tv for pc are large, that features its large 12-metre, deployable antenna. It’s kind of like deploying an umbrella in house, solely a really large one, so we can be on the lookout for that to occur easily,” mentioned Dr Cordey.
Airbus introduced in engineers from the American firm L3Harris Applied sciences to their website in Stevenage to supervise the development of the antenna-reflector.
L3Harris are specialists in these massive, unfurlable methods – experience which isn’t presently possessed in Europe.
 L3 Harris Applied sciences
L3 Harris Applied sciencesIf the launch is profitable, the workforce is hoping to supply the primary maps inside six months, and can then proceed to assemble information for the following 5 years.
These annual maps won’t solely present how a lot carbon is saved however how a lot is being misplaced by means of deforestation.
“The form of observations that we have had for 50 years from [other] satellites like Landsat are affected very closely by clouds. And in tropical areas, we have now clouds lots of the time, so you could not see a piece of tropical forest,” mentioned Prof Disney.
One other benefit of the longer wavelength of the Biomass satellite tv for pc is that it might penetrate clouds giving a constant, comparable view of a forest from one yr to the following.
It’s this end result which has motivated the scientists who’ve labored on the undertaking for greater than 20 years.
“It is thrilling, as a result of it should inform us about how one thing that we maybe take as a right,” mentioned Dr Cordey. “Our forests, our timber, how they’re contributing to the processes which govern our planet, and particularly, the processes behind local weather change that are so essential to us at the moment and for the longer term.”